Climate Change: An Inevitable Reality
Emergency Preparedness | Snohomish County Health Department, WA - Source snohd.org
Editor's Notes: "Climate Contingencies: Preparedness And Mitigation Strategies For A Changing World" have published today date. With the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters, it is crucial to prepare for and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Our team has meticulously analyzed and gathered information to present this comprehensive guide on climate contingencies, providing valuable insights to help you navigate this pressing issue.
Understanding climate contingencies and implementing effective strategies is essential for safeguarding our communities, economies, and ecosystems from the devastating effects of climate change. This guide explores the key aspects of climate preparedness and mitigation, empowering you to make informed decisions and contribute to a more resilient and sustainable future.
Key Takeaways:
| Preparedness | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Disaster planning and response | Reducing greenhouse gas emissions |
| Early warning systems | Promoting renewable energy sources |
| Community engagement and resilience | Enhancing energy efficiency |
FAQ
This section presents frequently asked questions and their answers on climate contingencies, providing essential information for preparedness and mitigation strategies.
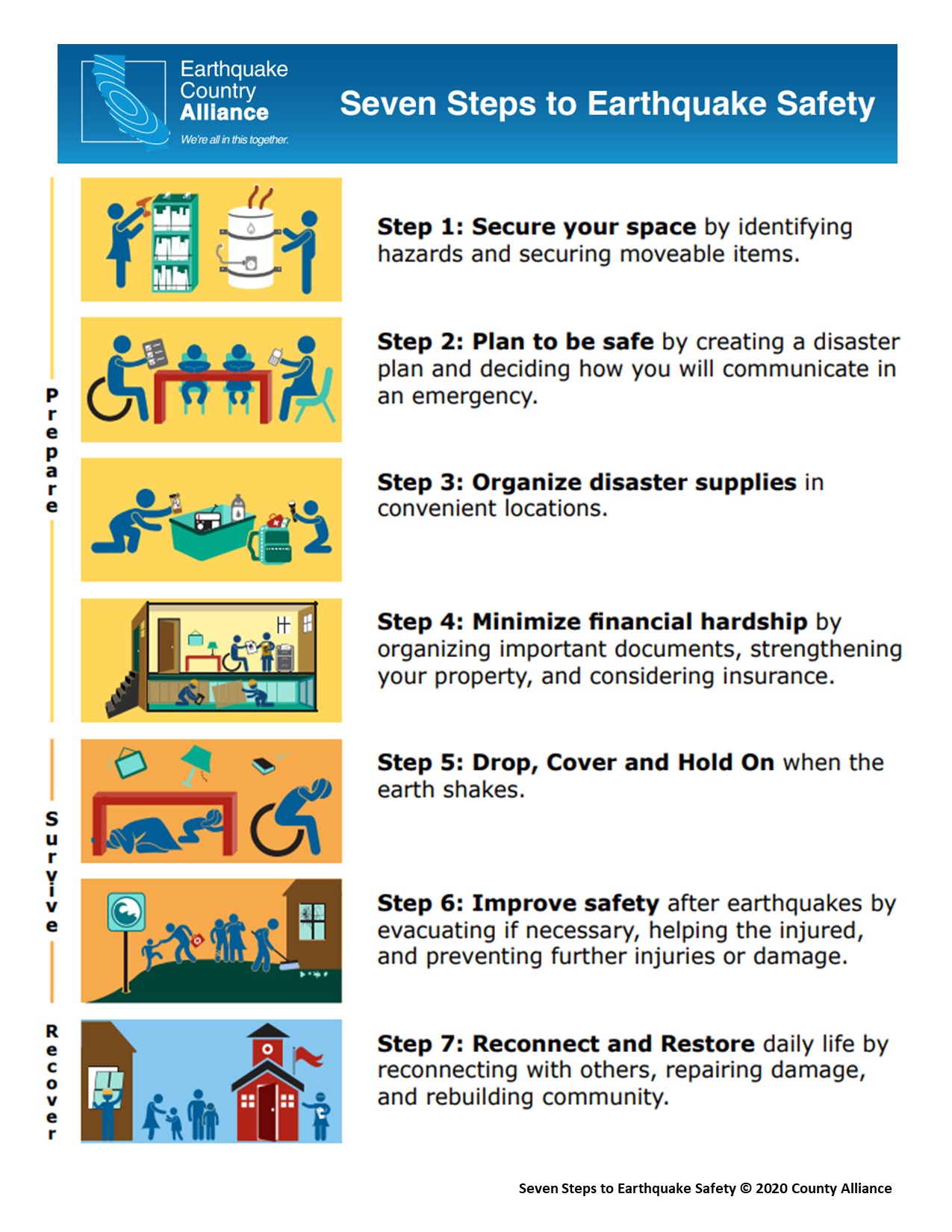
Are You Ready for an Earthquake? Bainbridge Island Fire Department - Source www.bifd.org
Question 1: What are the major climate contingencies that pose significant threats?
Answer: Climate contingencies encompass a range of extreme weather events and gradual environmental changes. These include rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, increased frequency of hurricanes and heat waves, rising sea levels, drought, and species extinction.
Question 2: How can we prepare for and mitigate the impacts of climate contingencies?
Answer: Preparedness involves implementing measures to minimize the adverse effects of climate contingencies. Mitigation involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices to lessen their intensity and frequency. Both strategies require collaboration among governments, scientists, businesses, and individuals.
Question 3: What are the long-term consequences of climate contingencies?
Answer: Climate contingencies can have profound long-term implications. Alterations in ecosystems and biodiversity can disrupt food chains and ecosystems. Sea-level rise and extreme weather events threaten coastal communities, infrastructure, and livelihoods. Prolonged droughts can lead to water scarcity and agricultural losses.
Question 4: What role do individuals play in addressing climate contingencies?
Answer: Individuals can contribute to preparedness and mitigation efforts by reducing their carbon footprint, adopting sustainable practices in their daily lives, and supporting policies that promote climate resilience. Education and awareness are crucial for encouraging collective action.
Question 5: How can we ensure equitable distribution of resources and opportunities in the face of climate contingencies?
Answer: Climate contingencies disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. Equitable distribution of resources, such as access to clean water, healthcare, and education, is essential for minimizing social and economic disparities. Inclusive decision-making and support systems are necessary for building resilient communities.
Question 6: What are the potential benefits of addressing climate contingencies?
Answer: Addressing climate contingencies offers opportunities for innovation, economic growth, and societal well-being. Transitioning to sustainable energy sources can create new jobs, improve air quality, and reduce healthcare costs. Climate-resilient infrastructure can enhance community resilience and minimize future losses.
Climate contingencies present daunting challenges, but by understanding their risks and implementing comprehensive preparedness and mitigation strategies, we can build a more sustainable and resilient future.
Moving forward, the article will delve into the specific strategies and policies that can be implemented to enhance our readiness for climate contingencies.
Tips
As outlined in Climate Contingencies: Preparedness And Mitigation Strategies For A Changing World, preparing and mitigating for climate change requires effective measures. Here are several tips to guide actions:
Tip 1: Conduct Vulnerability and Risk Assessments
Identifying vulnerabilities and risks is crucial for targeted preparedness and mitigation strategies. Assessments should consider potential climate hazards, exposure to risks, and the sensitivity and adaptive capacity of communities and ecosystems.
Tip 2: Develop and Implement Adaptation Plans
Adaptation plans provide a framework for implementing measures to reduce the adverse impacts of climate change. They should include short- and long-term strategies, such as infrastructure upgrades, land-use planning, and community-based adaptation initiatives.
Tip 3: Enhance Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems provide crucial lead time to prepare for and respond to climate hazards. They should be tailored to specific local contexts, consider multiple hazards, and include effective communication and response mechanisms.
Tip 4: Promote Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
Infrastructure, such as buildings, roads, and water systems, should be designed to withstand the impacts of climate change. This includes incorporating resilience measures into new infrastructure development and retrofitting existing structures to enhance their adaptive capacity.
Tip 5: Foster Community Engagement and Empowerment
Community engagement is essential for effective climate adaptation and mitigation. Empowering local communities through education, awareness-raising, and participatory decision-making processes enables them to take ownership of climate preparedness and response measures.
Tip 6: Strengthen Climate Monitoring and Research
Ongoing monitoring and research are vital for understanding climate change impacts, improving risk assessments, and evaluating the effectiveness of adaptation and mitigation strategies. This includes data collection, modeling, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Tip 7: Promote Sustainable Land and Water Management
Land and water resources are highly vulnerable to climate change impacts. Promoting sustainable management practices, such as conserving forests, protecting wetlands, and adopting water-efficient technologies, can enhance resilience and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Tip 8: Encourage Low-Carbon Transitions
Mitigating climate change requires reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved through promoting renewable energy sources, energy efficiency measures, sustainable transportation systems, and responsible land-use practices.
By implementing these tips, communities and governments can strengthen
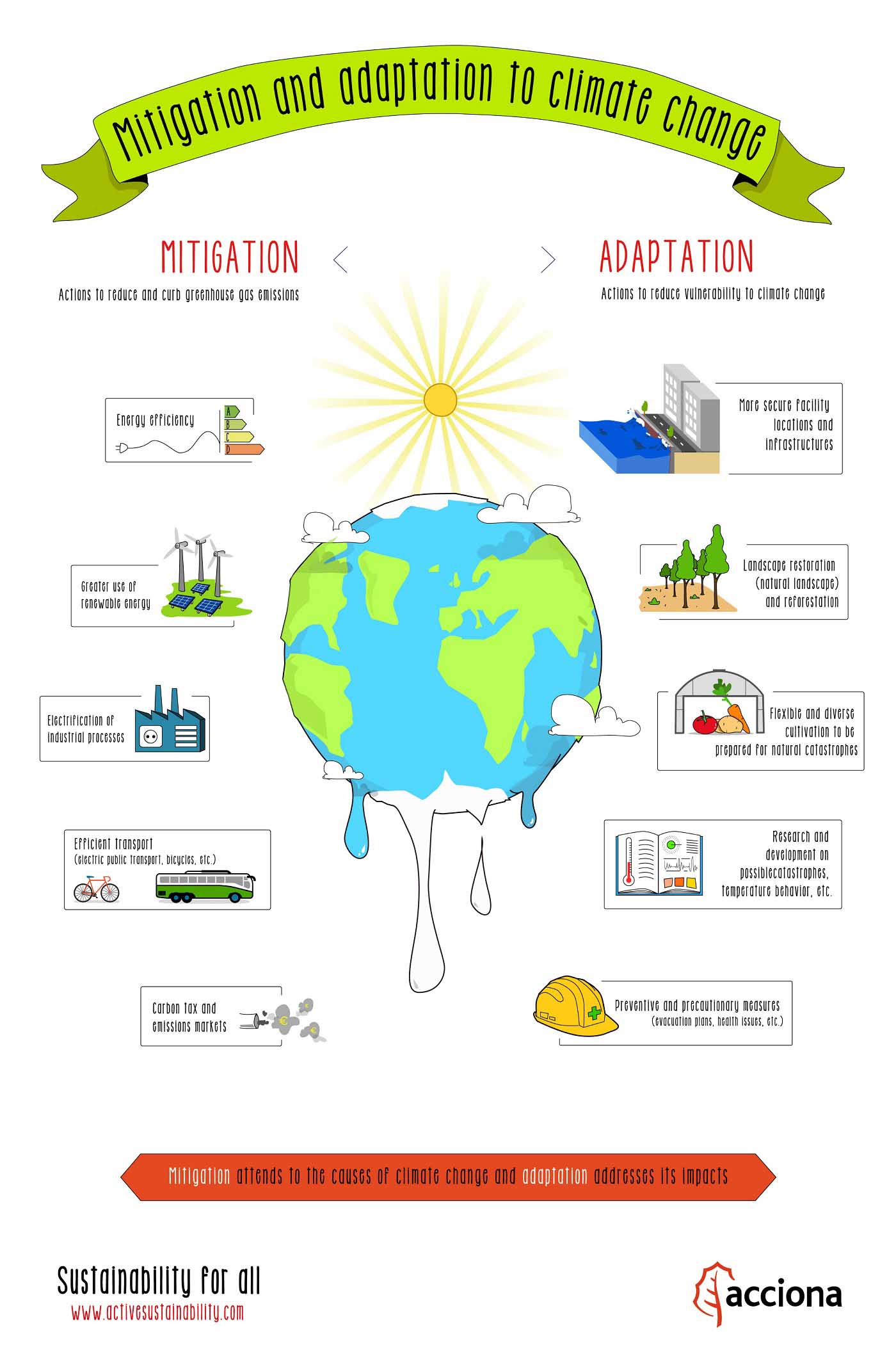
Mitigation and adaptation to climate change - Source www.activesustainability.com
their preparedness and adaptive capacity to the challenges posed by climate change.
Climate Contingencies: Preparedness And Mitigation Strategies For A Changing World
Climate contingencies demand proactive measures to safeguard communities and ecosystems. Preparedness and mitigation strategies encompass a multifaceted approach, focusing on early warning systems, resilient infrastructure, and sustainable practices.

Mitigation Strategies to Climate Change - Co2nsensus - Source wp.co2nsensus.com
- Early Warning: Timely information on impending climate events enables proactive responses.
- Resilient Infrastructure: Designing and reinforcing infrastructure to withstand climate impacts ensures continuity of essential services.
- Disaster Preparedness: Establishing robust emergency plans, training personnel, and stockpiling resources prepare communities for climate-related emergencies.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and evaluating climate risks helps prioritize mitigation measures and allocate resources effectively.
- Climate-Smart Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and water management practices mitigates climate change and enhances resilience.
- International Collaboration: Sharing knowledge, resources, and technologies across borders strengthens global response efforts to climate contingencies.
These key aspects are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. Early warning systems facilitate timely evacuations and resource mobilization during emergencies. Resilient infrastructure reduces economic losses and protects lives. Preparedness measures minimize the impacts of extreme weather events, while risk assessment guides decision-making and resource allocation. Climate-smart practices contribute to long-term resilience by reducing emissions and enhancing ecosystem services. International collaboration fosters knowledge sharing and strengthens collective action against climate contingencies.

Climate Change Mitigation: Policies and Lessons for Asia | Asian - Source www.adb.org
Climate Contingencies: Preparedness And Mitigation Strategies For A Changing World
Climate Contingencies: Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies for a Changing World" addresses a crucial subject that has far-reaching effects on the planet, people, and economies. Climate change is a major challenge that necessitates timely and intensive global action.

Satro - Climate Change - Source www.satro.org.uk
This article investigates the interconnectedness of preparedness and mitigation techniques, emphasizing the significance of adopting a comprehensive strategy to deal with climate-related dangers. Climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts are critical for reducing the severity and occurrence of climate-related disasters. Understanding the connections between these tactics empowers policymakers, organizations, and people to take proactive actions to lower climate change risks and build more resilient communities.
Climate Contingencies: Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies for a Changing World" also underlines the value of community resilience in the face of climate change. To efficiently prepare for and minimize the effects of climate-related catastrophes, the collaborative efforts of governments, organizations, and citizens are necessary. The report highlights successful case studies from around the world that highlight the effectiveness of preparedness and mitigation efforts. The article's insights can assist policymakers, practitioners, and the general public in taking informed action to minimize the impacts of climate change and construct a more sustainable future.
Table: Key Insights from "Climate Contingencies: Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies for a Changing World":
| Preparedness | Mitigation | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions taken to anticipate, prepare for, and respond to climate-related events | Actions taken to reduce or prevent the emission of greenhouse gases |
| Importance | Reduces vulnerability, protects lives and property, and facilitates recovery | Slows the pace of climate change and reduces the severity of its impacts |
| Examples | Early warning systems, disaster preparedness plans, resilient infrastructure | Renewable energy, energy efficiency, carbon capture and storage |
Conclusion
Climate Contingencies: Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies for a Changing World" serves as a call to action, emphasizing the critical need for proactive measures to address climate change. By integrating preparedness and mitigation techniques, we can strengthen our communities' resilience, safeguard lives and property, and build a sustainable future. While challenges remain, the insights and examples provided in the article empower us to take informed actions that will shape the course of our planet for generations to come.