The Paris Agreement: A Pivotal Framework for Mitigating Climate Change Globally
Editor's Note: The Paris Agreement: A Global Climate Change Mitigation Framework was published on [Today's Date]. This topic is critical to comprehend due to its profound implications for the planet's future and the well-being of its inhabitants.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we have crafted this comprehensive guide to the Paris Agreement: A Global Climate Change Mitigation Framework. Our aim is to empower individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
Key Differences and Takeaways
| Characteristic | Paris Agreement |
|---|---|
| Objective | Limit global temperature rise to 2 degrees Celsius, with efforts to limit it to 1.5 degrees. |
| Scope | Legally binding for all participating countries. |
| Implementation | Nationally determined contributions (NDCs) submitted by countries, outlining their emissions reduction efforts. |
FAQ: Paris Agreement: A Global Climate Change Mitigation Framework
The Paris Agreement on climate change is a landmark international treaty adopted in 2015 that aims to substantially reduce greenhouse gas emissions and limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, above pre-industrial levels.
What is the Paris Agreement? Here's all you need to know | World - Source www.weforum.org
Question 1: What are the Key Objectives of the Paris Agreement?
The Agreement aims to strengthen the global response to climate change by:
- Limiting global temperature rise to well below 2 degrees Celsius, pursuing efforts to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius,
- Increasing the ability of countries to deal with the impacts of climate change, and
- Making financial flows consistent with low-greenhouse gas emissions and climate-resilient pathways.
Question 2: Which Countries Have Signed and Ratified the Agreement?
As of 2023, 196 countries have signed the Agreement, and 193 have ratified it. The United States has rejoined the Agreement after withdrawing during the Trump administration.
Question 3: What is the Role of Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)?
NDCs are commitments made by individual countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. These contributions are updated every five years and form the backbone of the Paris Agreement.
Question 4: How is the Progress of the Paris Agreement Monitored?
The implementation of the Paris Agreement is monitored through a Global Stocktake process every five years. This process evaluates the collective progress towards the goals of the Agreement and considers areas where further action is needed.
Question 5: What are the Key Challenges to Implementing the Paris Agreement?
Implementing the Paris Agreement requires significant financial resources, technological advancements, and political will. Challenges include:
- Mobilizing sufficient climate finance,
- Developing and deploying low-carbon technologies,
- Addressing social and economic impacts of emissions reduction,
- Strengthening international cooperation.
Question 6: What are the Benefits of Implementing the Paris Agreement?
The benefits of implementing the Paris Agreement include:
- Mitigating the risks and impacts of climate change,
- Promoting sustainable economic growth,
- Improving air quality and public health,
- Enhancing energy security.
The Paris Agreement represents a pivotal step forward in the global response to climate change. Its implementation requires concerted efforts, collaboration, and unwavering commitment from all stakeholders.
Next Article: The Role of Renewable Energy in Mitigating Climate Change
Tips for Understanding and Acting on the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement: A Global Climate Change Mitigation Framework is a legally binding international treaty on climate change. The agreement was adopted by 196 parties at the 21st Conference of the Parties of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Paris and entered into force on 4 November 2016. The Paris Agreement's goal is to limit global warming to well below 2, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels. To achieve this long-term temperature goal, countries aim to reach global peaking of greenhouse gas emissions as soon as possible to achieve a climate-neutral world by mid-century.
Tip 1: Understand the Paris Agreement's Goals
The Paris Agreement has three main goals:
- Limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels.
- Increase the ability of countries to deal with the impacts of climate change.
- Make financial flows consistent with a pathway towards low-greenhouse gas emissions and climate-resilient development.
Tip 2: Know the Key Provisions of the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement includes a number of key provisions, including:
- Nationally determined contributions (NDCs): Countries are required to submit NDCs, which outline their plans for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Global stocktake: The global stocktake is a process that will be conducted every five years to assess the collective progress towards achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- Finance: Developed countries are committed to providing financial support to developing countries to help them implement their NDCs.
Tip 3: Be Aware of the Challenges to Implementing the Paris Agreement
There are a number of challenges to implementing the Paris Agreement, including:
- The need for ambitious NDCs: Countries need to submit ambitious NDCs that are in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- The need for financial support: Developing countries need financial support to implement their NDCs.
- The need for political will: Governments need to have the political will to implement the Paris Agreement.
Summary
The Paris Agreement is a landmark agreement that has the potential to make a significant contribution to the fight against climate change. However, there are a number of challenges to implementing the agreement. By understanding the goals, key provisions, and challenges of the Paris Agreement, we can all play a role in ensuring that it is successfully implemented.
Paris Agreement: A Global Climate Change Mitigation Framework
The Paris Agreement, a landmark accord, aims to tackle climate change by setting a framework for global mitigation actions. Its key aspects, ranging from targets to implementation, are crucial to understanding its efficacy.
- Ambitious Goals: Limit global warming to well below 2°C, pursuing efforts towards 1.5°C.
- National Commitments (NDCs): Countries' voluntary pledges to reduce emissions, updated over time.
- Transparency and Review: Regular reporting, monitoring, and verification of progress to foster accountability.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Promoting climate change adaptation measures to enhance community resilience.
- Finance and Technology Transfer: Facilitating financial and technical support for developing countries to mitigate emissions and adapt to climate impacts.
- Loss and Damage: Addressing residual climate impacts that cannot be avoided or adapted to, particularly in vulnerable communities.
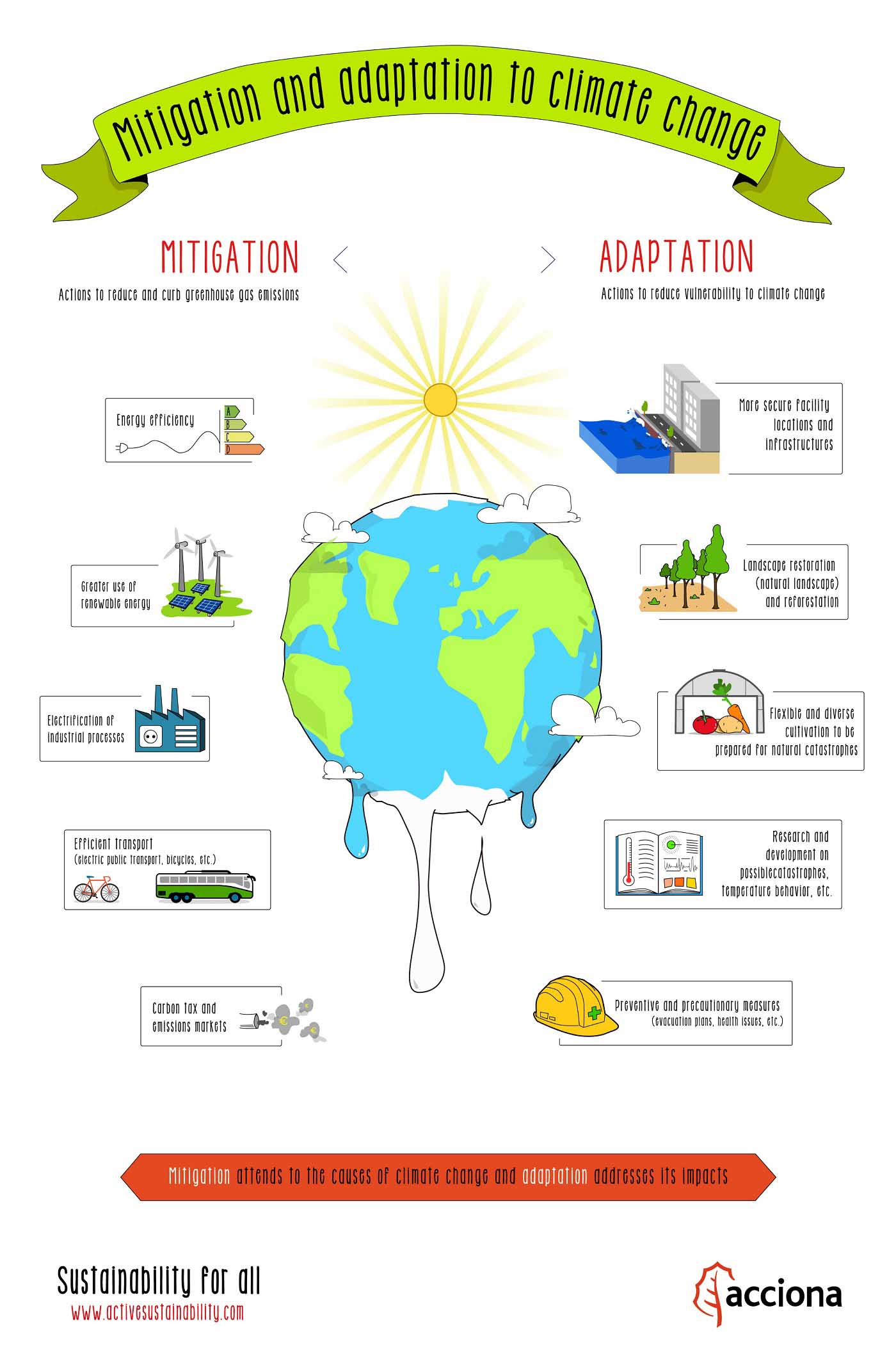
Mitigation and adaptation to climate change - Source www.activesustainability.com
These key aspects collectively form the backbone of the Paris Agreement, guiding efforts to address climate change. By setting ambitious goals, establishing national commitments, promoting transparency and review, supporting adaptation and resilience, facilitating finance and technology transfer, and acknowledging the need to address loss and damage, the agreement aims to foster global collaboration and drive meaningful actions towards a sustainable future.
Paris Agreement: A Global Climate Change Mitigation Framework
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, sets ambitious goals for mitigating global climate change. It establishes a framework for nations to collaborate and decrease greenhouse gas emissions while promoting the transition to renewable energy. The agreement emphasizes the importance of equity, climate justice, and the protection of vulnerable populations.
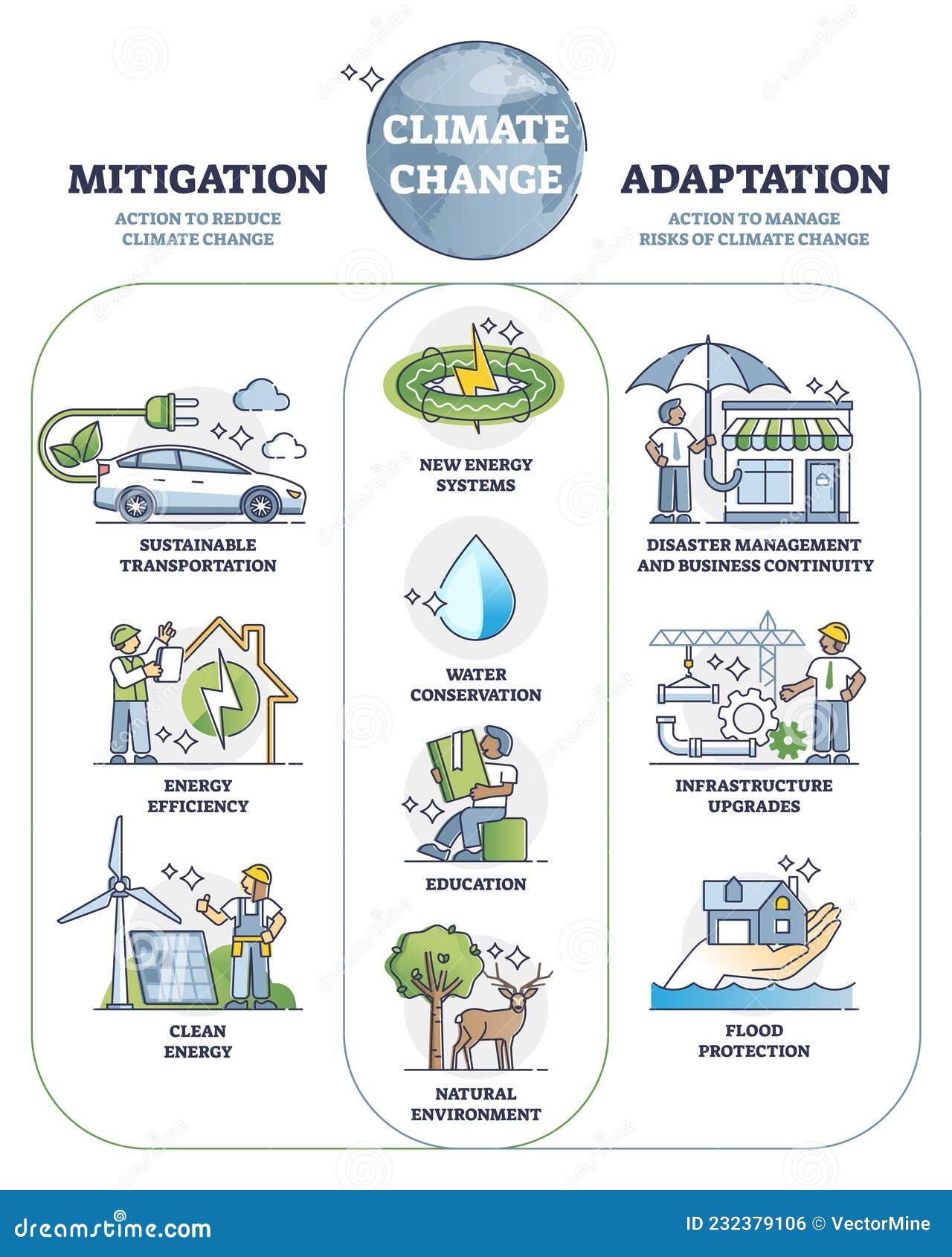
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Actions for Future Outline - Source www.dreamstime.com
The Paris Agreement is crucial for addressing climate change because it provides a comprehensive plan for transitioning to a low-carbon society. Its emphasis on adaptation and resilience measures ensures that vulnerable communities are supported and empowered to face the effects of climate change. The agreement has been endorsed by 197 countries, and its implementation is critical for ensuring a sustainable future for our planet.
The practical significance of understanding the Paris Agreement lies in its potential to shape global climate action. By providing a shared framework and ambitious goals, it creates a common ground for nations to collaborate and establish effective policies. The agreement serves as a roadmap for reducing emissions, adapting to climate impacts, and ensuring a just and equitable transition to a sustainable future.
Insights Table:
| Concept | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| Mitigation Framework | Comprehensive approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Equitable Transition | Prioritizes climate justice and support for vulnerable populations. |
| Adaptation and Resilience | Emphasizes measures to cope with and recover from climate change impacts. |
| Global Collaboration | Encourages international cooperation and shared responsibility. |
Conclusion
The Paris Agreement stands as a testament to the global commitment to addressing climate change. Its transformative potential lies in its ability to guide nations toward a sustainable future. By fostering collaboration, promoting innovation, and emphasizing equity, the Paris Agreement sets a path for reducing emissions, adapting to climate impacts, and ensuring a just transition to a cleaner, greener world.
The practical application of the Paris Agreement requires ongoing commitment, innovation, and collaboration. As nations work together to implement its provisions, we can expect to see advancements in renewable energy technologies, energy efficiency measures, and climate adaptation strategies. The full realization of the Paris Agreement's goals will not only mitigate the effects of climate change but also create a more sustainable and prosperous society for generations to come.
